Principle of Polymerization
Compounds of acrlic monomer/functional monomer at different glass transition temperature could be prepared into functional acrylic macromoleclar polymer through free radical polymerization, which is triggered by radical initiator. The polymer has good tack and build-up adhesion, could be used as adhesive. Meanwhile, it has good resistance to climate, heat and water, so it's widely applied in industrial manufacturing like mobile phone, home appliance, vehicle and medical device.
After polymerization reaction, some tackifying resin or functional additives like fire retardant, conducting particles, etc. could be added to make adhesive more functional.
To ensure coating fluidity of acrylic polymer, cross-linking agent (like isocyanates or epoxy resin) would be mixed up during tape coating, so that acrylic polymer will have 3-D network open cells structure.
Reactive Monomer
|
Monomer Type |
Chemical Name (Abbreviation) |
Molecule |
Glass Transition Temperature |
|
Main Monomer |
Butyl Acrylate〔BA〕 |
CH2=CHCOOC4H9 |
-22 |
|
Ethyl Acrylate〔EA〕 |
CH2=CHCOOC2H5 |
|
|
|
2-ethylhexyl acrylate 〔2-EHA〕 |
CH2=CHCOOCH2CH(C2H5)C4H9 |
-70 |
|
|
Comonomer (cohesion improvement) |
Vinyl Acetate〔VAc〕 |
CH2=CHOCOCH3 |
32 |
|
Acrylonitrile〔AN〕 |
CH2=CHCN |
97 | |
|
Styrene〔St〕 |
CH2=CHC6H5 |
100 | |
|
Methyl Methacrylate〔MMA〕 |
CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3 |
-50 | |
|
Functional Monomer (Introducing —COOH—OH bridging group) |
Acrylic Acid〔AA〕 |
CH2=CHCOOH |
106 |
|
Methacrylic Scid 〔MAA〕 |
CH2=C(CH3)COOH |
228 | |
|
2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate〔2-HEA〕 |
CH2=CHCOOCCH2CH2OH |
-60 | |
|
2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate〔2-HEMA〕 |
CH2=C(CH3)COOCH2CH2OH |
-12 | |
|
Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate 〔DM〕 |
CH2=C(CH3)COOCH2CH2N(CH3)2 |
-50 | |
|
Acrylic Amide〔AM〕 |
CH2=CHCONH2 |
165 | |
|
Glycidyl Methacrylate〔GMA〕 |
CH2=C(CH3)COOCHCH-CH2 |
-82 |
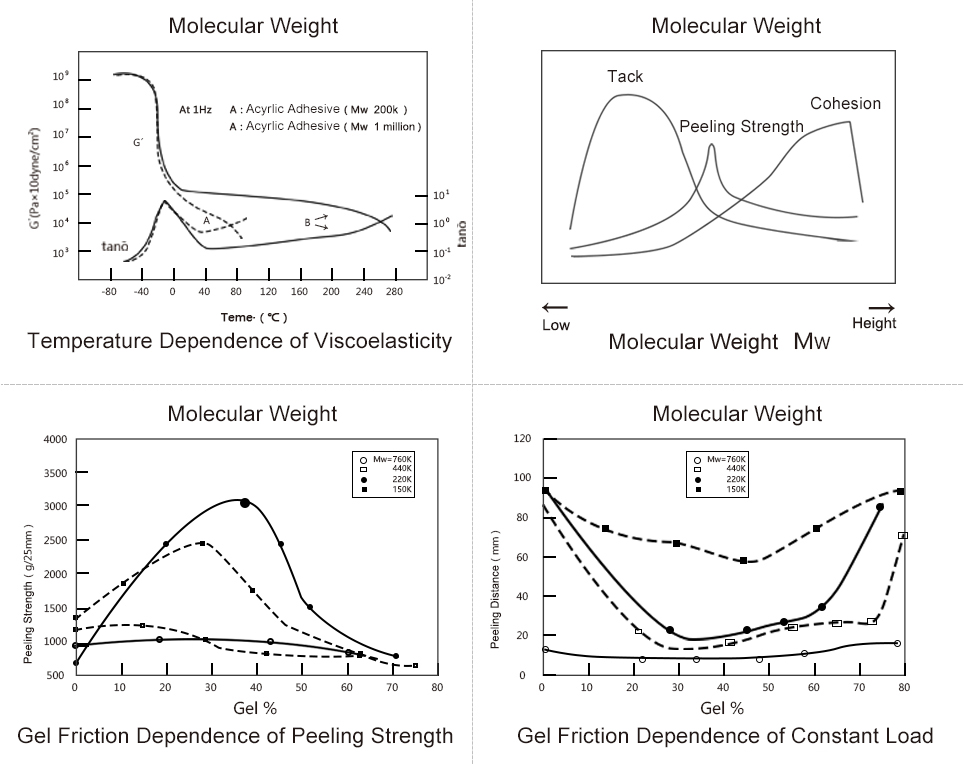
Performance Analysis